Viniliquid™: A Versatile and Efficient Fermentation Aid
What is ViniLiquid™ and why should you use it?
ViniLiquid™ is a highly innovative fermentation activator developed by Fermentis in order to optimize fermentation performance, especially in the case of nutrient-poor musts. It is a highly degraded autolyzed yeast offering the advantages of both soluble yeast intracellular content and insoluble yeast hulls. ViniLiquid’s unique composition helps you improve and secure fermentation thanks to its:
- strong supply of essential amino acids that drastically increase YAN (Yeast Available Nitrogen) level;
- supply of growth and survival factors;
- detoxification properties and support effect; and
- unique liquid formulation that makes it easily and directly dispersible into the must, pumpable, and safe (no risk of yeast powder inhalation).
As such, it was Fermentis’ first Easy To Use (E2U™) yeast derivative.
Fermentation improvement using ViniLiquid
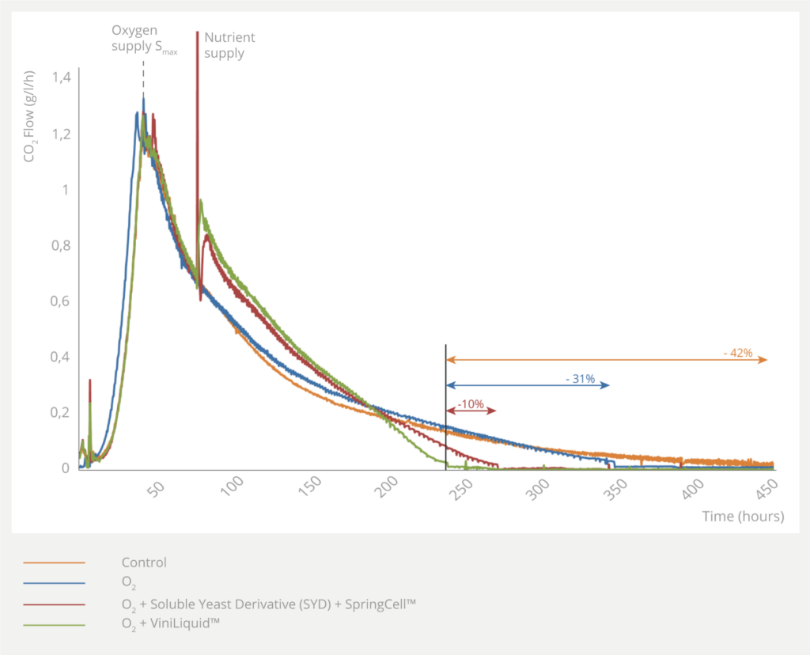
Fermentation times using different activators
Chardonnay must (Potential ABV: 12.5%, pH 3.4 and initial YAN: 188mg/L). Addition of 10mg/L of O2 at maximum fermentation speed (Smax) then equivalent supply of 20mg/L of YAN and 13.4g/hL of hulls through ViniLiquid single addition or mix of soluble yeast
While the addition of O2 alone (blue line in the graph) decreases fermentation time, it is clear that adding a mix of yeast derivative and Fermentis SpringCell™ (red line) is a lot more efficient. But undoubtably, the most efficient way to speed up and secure fermentation is through the addition of O2 and ViniLiquid, which can decrease fermentation time by up to 42% when compared to the control fermentation. There are strong synergistical effects between O2 and ViniLiquid together. However these results show that ViniLiquid is more powerful than a dry yeast autolysate with a similar composition, thus reinforcing the point of leaving it liquid.
> Key lessons
ViniLiquid strongly helps decrease fermentation time compared to other yeast-derived dry fermentation aids. It acts synergistically with O2 supply.
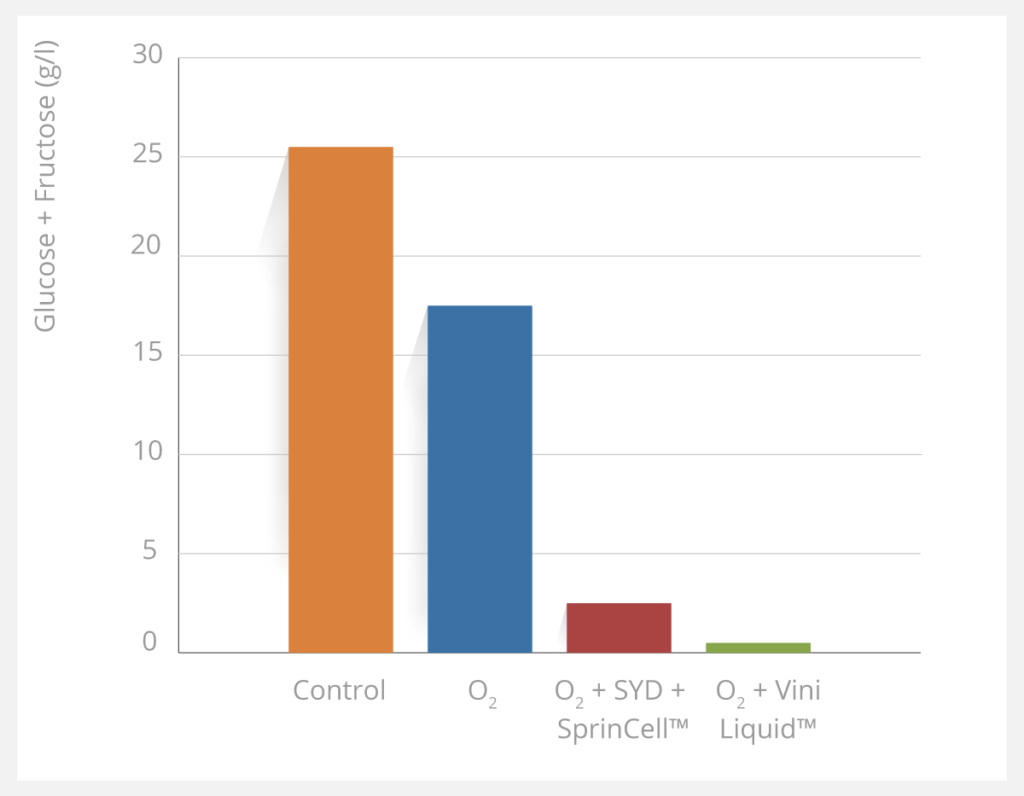
Residual sugars after 238h of fermentation
The graph above shows that after 238h of fermentation, the combination of O2 and ViniLiquid led to a fully complete fermentation (0.50g/L of residual sugars) and clearly illustrated that in this must, O2 supply alone was not sufficient to achieve the fermentation whereas the combination with dry yeast derivatives achieved fermentation a bit later.
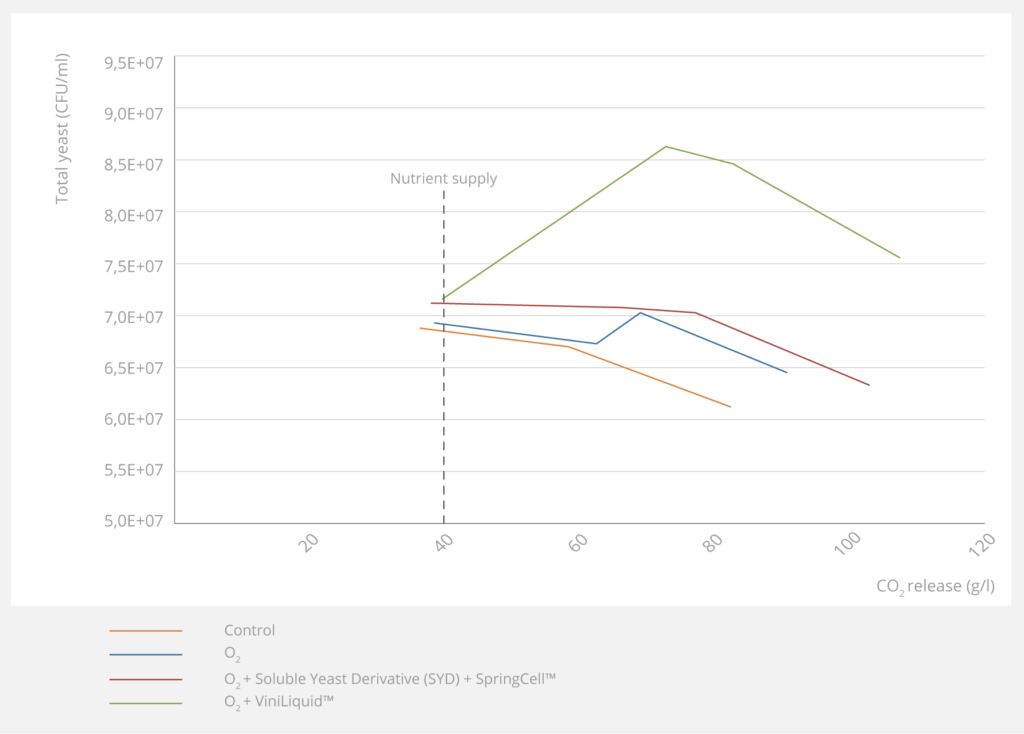
On this yeast viability graph, the addition of nutrients shows an effect on yeast population, with one stand-out winner: ViniLiquid, which generates a surge in yeast population, whereas other nutrients yield only weak results. ViniLiquid, like much of Fermentis’ yeast derivative range, is E2U™ certified, meaning it’s very easy and safe to use.
> Key lessons
ViniLiquid leads to a more important cellular regrowth and viability maintenance than the combined additions of yeast derivatives and hulls. According to its fermentative power, Fermentis recommends: 50mL/hL of ViniLiquid for an equivalent YAN supply of 20 mg/L.
Yeast viability
Gros Manseng must (Potential ABV: 13.5%, pH 3.1 and initial YAN: 115mg/L).10mg/l O2 at Smax, then equivalent supply of 35mg/l of YAN and 19.2g/hl of hulls through ViniLiquid single addition or mix of soluble yeast derivative and Fermentis SpringCell yeast hulls addition at 1/3rd of the fermentation advancement. Yeast used: Fermentis SafŒno CK S102.
